
What is cellulite?
Cellulite is not normal body fat, or unique to overweight people as even slim women can get it. This hail damage effect is commonly found on the thighs, hips, bottom and stomach. However, there is plenty you can do about it ...
Cellulite is considered a cosmetic defect, not a disease or a disorder. It appears as lumpy skin because of the following defects within the skin:
- disordered fat cells in the fatty (subcutaneous) layer of your skin
- irregular connective tissue in the deeper (dermis) layer of the skin, which allows the fatty layer to intrude into the dermis, making skin appear lumpy (refer to “What is connective tissue?”, below).
Why does cellulite affect women more often than men?
It afflicts women more often that men because men have a genetic tendency for stronger connective tissue in the dermis layer of the skin.
Unfortunately, women are more likely to have irregular connective tissue immediately below the skin, making us more prone to getting disorderly connective tissue fibres that lose flexibility and movement, similar to when an old swimsuit loses its elasticity and no longer fits snugly. This tissue weakness allows the fatty layer (the subcutaneous layer) just below the skin’s deep dermis layer to protrude into the dermis, which makes the skin look lumpy.
You can perform your own skin pinch test to see if you have underlying cellulite (stage 1) ...
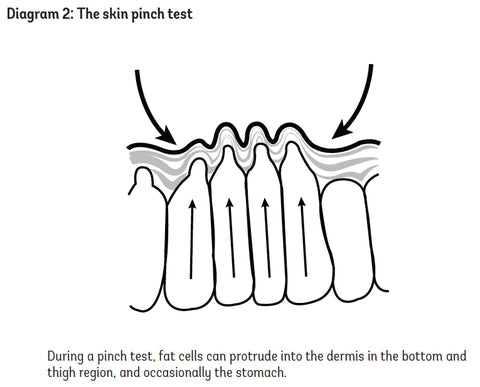
Although cellulite occurs in varying degrees in as many as 85% of women, not all women get cellulite and it’s from these ladies that we can gain hope and also a bit of insight into how to avoid cellulite in future.
What causes cellulite?
- genetics (being female) and hormones
- poor circulation
- sedentary lifestyle (not exercising)
- diets high in dairy products, salt and sugar (modern western diets!)
- environmental pollution, chemicals, toxins
- nutritional deficiencies
What is connective tissue?
You wouldn’t want your liver to dislodge and squash an artery, blocking off your valuable blood supply, would you? Luckily you have connective tissue, which is a fibrous material that literally connects your muscles and organs to one another so they can’t aimlessly move around the body.
This ‘cellular glue’ also helps bring nutrients to the tissues and gives tissues form and strength. Without good connective tissue the skin becomes fragile and sags.
Connective tissue is where you find the famous beauty materials collagen and elastin: both provide the skin with strength, the ability to stretch and the capacity to return to its original shape after extension (this is the ideal scenario). If the connective tissue doesn’t return to its normal shape it becomes irregular and cellulite can occur.
Connective tissue can also tear if it hasn’t been supplied the right skin nutrients (such as the mineral zinc), causing stretch marks to appear.
Toxins from pollution, poor diet and cigarette smoke are absorbed into the body and can become lodged around connective tissues. If you eat a poor diet that doesn’t supply enough collagen enhancing nutrients (vitamin C, silica, manganese, zinc etc.), connective tissue loses strength and your skin eventually sags. Sagging skin is common when overweight people follow poorly designed diets that consist of nothing but salads.
Top 5 natural cellulite remedies
- Frequent exercise – improves blood flow to the skin and helps remove toxins via your lymph.
- Take a calcium supplement – calcium helps to tighten muscles and it thickens the skin barrier which helps to visibly reduce the appearance of cellulite.
- Massage – helps to reduce water retention, improve lymphatic drainage and increase collagen synthesis
- Cut your salt intake – this reduces fluid retention and works remarkably well to reduce cellulite. TIP: Cut down on salt gradually as you may temporarily get low blood pressure which can make you feel dizzy at times – you do need some salt in your diet but not the kind from a salt shaker added to your meals each day, or the kind in packaged or canned foods.
- Eat a healthy diet – avoid dairy products and cut the sugar in your diet, as they contribute to the formation of cellulite. Dairy products supply animal hormones, which can disrupt your own hormone levels, and contributes to a sluggish lymphatic system (your lymph removes toxins from your tissues). Sugar consumption causes glycation damage in the skin and both are not good for your skin health. If you are going dairy-free, remember to take a calcium supplement.
FAQ: “Do weight-loss or anti-cellulite skin creams prevent cellulite?”
Research shows that weight-loss does not usually prevent cellulite. Being over-weight is often associated with cellulite as it can be caused by many of the same factors, such as too much salt- and sugar-rich foods in the diet. Research shows that salt- and sugar-rich foods contribute to over-eating, and they are condiments that greatly contribute to the appearance of cellulite. In reality, they are two separate symptoms caused by similar genetic, diet and lifestyle factors.
Good anti-cellulite skin creams usually plump up the skin to help temporarily reduce the appearance of cellulite. However, the effects usually wash off and they do not usually fix the root of the problem – i.e if you are still frequently consuming salt, sugar and dairy you will still have an underlying cellulite problem. Our top 5 natural cellulite remedies work incredibly well and they have transformed the appearance of my skin, even after having two children (see top 5 list above, plus the next tips on nutrients for preventing cellulite).
Nutrients for preventing cellulite
Collagen and elastin are made up of amino acids such as glycine and proline and a substance called hyaluronic acid. Hyaluronic acids main building block is glucosamine, which can normalise cartilage and restores joint function. Magnesium is also needed to manufacture hyaluronic acid and studies have shown that deficiencies in zinc and magnesium contribute to hyaluronic acid abnormalities.
Along with your healthy, anti-cellulite diet, also supplement with glucosamine, vitamin C, copper (if necessary), manganese, magnesium and zinc to improve elasticity and connective tissue strength.
References



 Nothing will be posted on your behalf.
Nothing will be posted on your behalf.

Excellent article. Concise but dense with helpful essential information. Thank you.